does a blo0ood test detect testicular torsion|blood test for testicular torsion : vendor Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which brings blood to the testicle from the abdomen. If the testicle rotates several times, blood flow to . Resultado da 14/08/2022. Londrina x Bahia. Confira prognóstico e palpite para Londrina x Bahia, que se enfrentam nesta terça-feira (16), às 20h30 (horário de .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Nothing Phone (2) 让科技游戏再升级。透过增强版相机规格捕捉令人惊艳的照片,透过尖端 Glyph Interface 实现流畅互动,并体验 Nothing OS 2.0 的强大功能。以永续发展为考量,这款创新产品结合了创新与责任感。
urine test for testicular torsion
Decreased blood flow to the testicle is a sign of testicular torsion. But ultrasound doesn't always detect the reduced blood flow, so the test might not rule out testicular torsion. Surgery. Surgery might be necessary to determine whether your symptoms are caused by .Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which . Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which brings blood to the testicle from the abdomen. If the testicle rotates several times, blood flow to .
Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. This is a urological emergency; .
ultrasound testing for testicular torsion
testicular torsion test score
You might get one or more of these tests to diagnose testicular torsion: Urine test (checks for an infection) An imaging test of your scrotum, usually an ultrasound that uses . Ultrasound is a sensitive and specific test for the evaluation of testicular torsion. Early urology involvement is crucial to avoid testicular loss. The use of color flow is essential in . Testicular torsion is a medical emergency — it occurs when blood flow to the testicle stops, causing sudden and often severe pain and swelling. Testicular torsion is most common during .
Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, .
Testicular torsion is the twisting of a testis on its spermatic cord so that the blood supply to the testis is blocked. Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and . Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding. Testicular torsion is a very serious condition and is considered a medical emergency. Rotation of the testicle around the spermatic cord can cause obstruction of the arterial blood flow to the testicle, as well as the venous .
Laboratory tests are unlikely to be of consequence, as no single test has high sensitivity or specificity in diagnosing testicular torsion. . Radionuclide scans have a sensitivity of 90-100% in detecting testicular blood flow. Previous Next: . et al. Development and initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in . Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. This is a urological emergency; early diagnosis and treatment are vital to saving .
concrete moisture meter rental
Testicular torsion is a time-sensitive diagnosis that requires prompt surgical intervention to avoid testicular ischemia, infertility, and unwanted litigation. When imaging is required, the recommended and most available modality to detect torsion is ultrasonography. In pediatric patients, the use of SMI is supported.
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord becomes twisted. This causes a restriction in blood flow to the testes, severe pain, and possibly permanent damage. Find out what causes this .Testicular torsion is a painful twisting of a boy’s testicles and spermatic cord. Torsion causes blood to not flow to the testicles. . He may also have tests, such as an ultrasound. This is a painless imaging test that uses sound waves to see the scrotum and testicles and check blood flow. How is testicular torsion treated in a child?Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates and twists inside the scrotum, choking the blood flow through the arteries and veins. Without proper blood flow, the testicle can die. This twisting may occur due to rapid growth during puberty; about 65% of cases of testicular torsion occur in adolescents ages 11-19.A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes).
Testicular torsion is when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that provides it with blood and oxygen. Unless the injury is repaired within four to six hours, the loss of blood flow can irreparably damage the testicle, causing what is .Urine tests or blood tests. These can find if the pain and symptoms are being caused by an infection instead of a torsion. Sometimes, doctors will need to do surgery to be sure a problem is testicular torsion. A doctor may also do immediate surgery without any other testing in order to save the testicle.
The test can show if you have testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is a twisting of the testicle that can cut off blood flow. If ultrasound with color Doppler shows lower blood flow to a testicle than is typical, the testicle is twisted. If blood flow is higher than typical, this can help confirm that you have epididymitis.Blood tests for tumor markers. Some blood tests can help diagnose testicular tumors. Many testicular cancers make high levels of certain proteins called tumor markers, such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). When these tumor markers are in the blood, it suggests that there's a testicular tumor. Alternatively, testicular torsion was confirmed in five of the 11 patients (46%) in the group with diminished testicular blood flow, and in four of the 11 patients (36%) in the group with normal or increased testicular blood flow. Characterizing torsion by either the absence of or diminished, testicular blood flow in the CDUS evaluation, the .
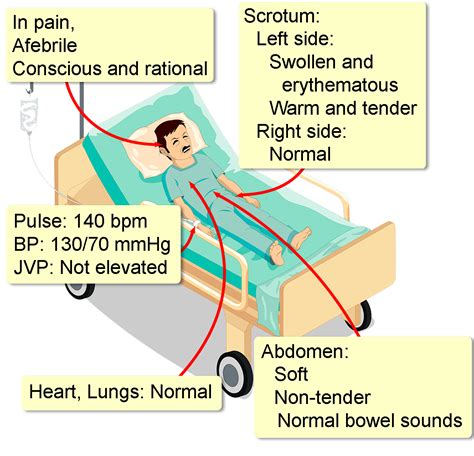
This is a painful condition caused by the twisting of the spermatic cord, which causes a loss of blood flow to the testicle. Testicular tissue cannot survive without blood flow. Torsion is the most common cause of testicle loss in adolescent males. . What Are the Exams and Tests to Diagnose Testicular Torsion?
Because extrinsic compression of the testicular parenchyma or spermatic cord can compromise inflow and outflow, one should evaluate for fluid collections around the testis and pathologic findings along the inguinal canal, .
Each year, testicular torsion affects one in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. Early diagnosis and definitive management are the keys to avoid testicular loss. All prepubertal and young adult . Testicular torsion treatment. To diagnose testicular torsion, a doctor (often a urologist) evaluate the groin and scrotum area. The doctor will also check the abdomen. You may need an ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis. .
Another way to diagnose testicular torsion is by checking for the cremasteric reflex by pinching or stroking the inner thigh on the affected side. Normally, this reflex causes the testicle to contract and rise, but it is often absent in individuals with testicular torsion. Additional tests that may be performed include urine analysis, as well .Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency with a yearly incidence of 3.8 per 100,000 males under the age of 18 [1]. The morbidity associated with testicular torsion is significant as 42% of surgeries result in orchiectomy [1]. However, testicular salvage rates are 90% to 100% if intervention is performed within 6 hours of symptom onset [2]. Introduction. Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord and its contents twists within the tunica vaginalis, compromising the blood supply to the testicle.. Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency, as without treatment the affected testicle will infarct within hours.Whilst theoretically it can occur at any age, peak incidence is in neonates and . Routine testicular self-exams can give you a greater awareness of the condition of your testicles and help you detect changes. Self-exams can also alert you to potential testicular problems. . Depending on the circumstances, your doctor might do a testicular exam followed by a blood test, ultrasound or biopsy. Most changes in your testicles .
But however sonology done on follow-up even after 15 days persisted to show left testicular torsion without any blood flow (Fig. 1A-C); hence this time scrotal exploration was done, which revealed bilaterally normal testis and cord structures without any kind of inflammation or loss of vascularity. Baby is doing well and is on follow-up with us.Main tests for testicular cancer. If the GP refers you to a specialist, you may need more tests and scans to check for testicular cancer. Tests you may have include: blood tests; an ultrasound scan of your testicles; Getting your results. It .
What is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion happens when one of your testicles twists around. Each testicle is attached to a spermatic cord, which contains blood vessels that carry blood to the testicle. In testicular torsion, this becomes twisted (called torsion) and blocks the flow of blood to the testicle. Testicular torsion is an emergency. Testicular torsion, also termed torsion of the spermatic cord, is a relatively common and potentially devastating acute condition resulting from obstruction of the arterial blood supply to the testis. [] Fortunately, this entity is relatively well known, and it usually occurs with enough discomfort to lead to its diagnosis and subsequent testicular salvage.
↑ Blaivas, M, et al. Emergency evaluation of patients presenting with acute scrotum using bedside ultrasonography. Academic Emergency Medicine. 2001; 8(1):90-93. ↑ Barbosa, JA, et al. Development of initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in children. The Journal of Urology. 2013; 189:1853-8. ↑ Gordon J, Rifenburg RP. . Spermatic Cord . MRI, however, is not a practical choice to diagnose testicular torsion given its limited availability, length of study, and cost. Scrotal scintigraphy. Scrotal scintigraphy is a nuclear study in which a radioisotope is used to demonstrate testicular blood flow. Although it used to be widely utilized starting in 1971, it has been replaced by .
testicular torsion lab workup
SHBET Thế Giới Casino Trong Tay Bạn, thương hiệu uy tín, sản phẩm đa dạng, an ninh bảo mật, giao dịch nhanh chóng, dịch vụ chăm sóc khách hàng chuyên nghiệp 24/7.
does a blo0ood test detect testicular torsion|blood test for testicular torsion